What is physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy is a medical practice that involves the treatment of physical conditions and injuries using various methods such as exercises, massage, heat therapy, and stretching. The goal of physiotherapy is to help patients recover from injuries, manage chronic pain, and prevent future injuries. In this article, we will focus on physiotherapy treatment and exercises.
Physiotherapy Treatment
Physiotherapy treatment is designed to address a variety of physical conditions and injuries. It is frequently used to treat musculoskeletal conditions such as back pain, neck pain, and joint pain. Physiotherapists also treat neurological conditions such as stroke, Parkinson’s disease, and multiple sclerosis. The treatment plan may include a combination of exercises, manual therapy, and modalities such as heat or ice therapy.
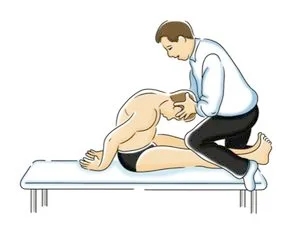
- Manual Therapy: Manual therapy is a hands-on treatment approach that involves the use of various techniques to manipulate the joints, soft tissues, and muscles. Manual therapy may involve massage, joint mobilization, and stretching. Manual therapy is used to improve the range of motion, reduce pain and inflammation, and improve muscle function.

- Exercises: Exercise is a key component of physiotherapy treatment. It is used to improve strength, flexibility, and endurance. Exercises may be prescribed to improve balance and coordination, prevent future injuries, and improve overall fitness. The type of exercise prescribed will depend on the patient’s condition and goals.
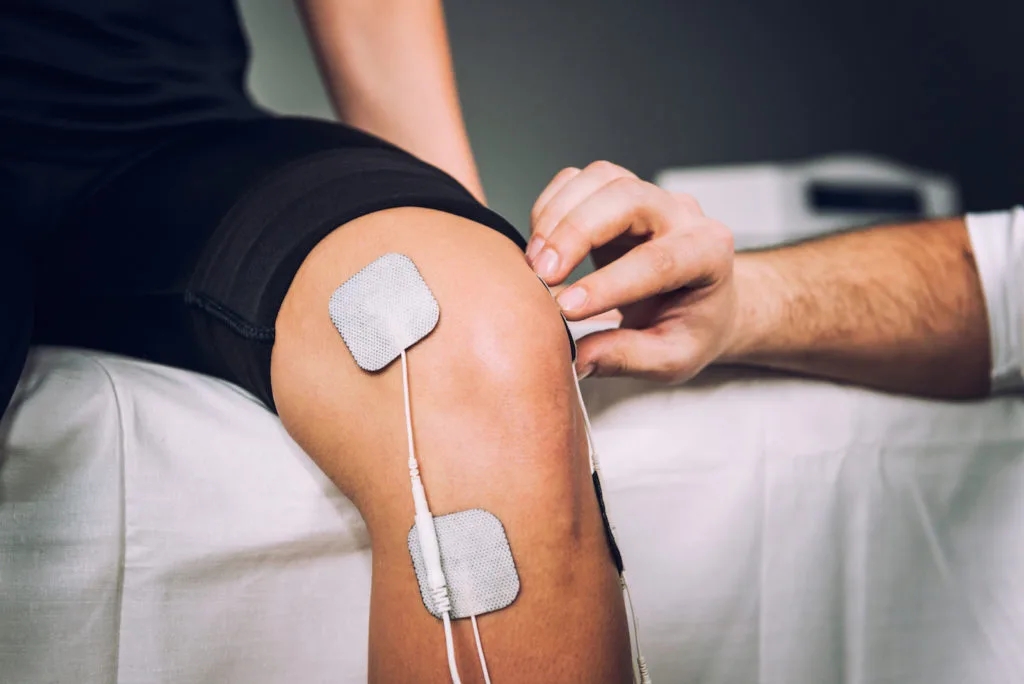
- Modalities: Modalities are treatments that are used in addition to exercises and manual therapy. These may include heat therapy, cold therapy, ultrasound, and electrical stimulation. Heat therapy is used to improve blood flow and reduce muscle tension, while cold therapy is used to reduce inflammation and pain. Ultrasound and electrical stimulation are used to promote healing and reduce pain.
- Education and Counseling: Physiotherapists often provide education and counseling to their patients on topics such as proper body mechanics, posture, and injury prevention. This can help individuals prevent future injuries and improve their overall health and well-being.
- Rehabilitation: Rehabilitation involves a combination of manual therapy, exercise therapy, and education to help patients recover from injuries or surgery, improve mobility and function, and return to their daily activities. Rehabilitation programs are typically tailored to each patient’s specific needs and may involve multiple treatment modalities.
Physiotherapy Exercises
Physiotherapy exercises are designed to improve mobility, strength, and flexibility. The type of exercise prescribed will depend on the patient’s condition and goals. Here are some common physiotherapy exercises:
- Range-of-motion exercises: Range-of-motion exercises are designed to improve the flexibility and mobility of joints. These exercises include moving the joints through their full range of motion. Range-of-motion exercises may be done passively, with the physiotherapist moving the joint, or actively, with the patient moving the joint.
- Strengthening Exercises: Strengthening exercises are designed to improve muscle strength. These exercises may involve the use of resistance bands, weights, or body weights. Strengthening exercises may be prescribed for specific muscle groups or for the whole body.
- Balance Exercises: Balance exercises are used to improve balance and coordination. These exercises may involve standing on one leg, walking on a balance beam, or using a balance board.
- Cardiovascular Exercises: Cardiovascular exercises are designed to improve cardiovascular fitness. These exercises may include walking, jogging, or cycling. Cardiovascular exercises may be prescribed for patients with chronic conditions such as heart disease or diabetes.
- Stretching Exercises: Stretching exercises are designed to improve flexibility and reduce muscle tension. These exercises may involve static stretching or dynamic stretching. Static stretching involves holding a stretch for 20-30 seconds, while dynamic stretching involves moving through a movement.
Goals of physiotherapy
The goals of physiotherapy treatment vary depending on the individual’s condition, but generally include the following:
- Reduce Pain: One of the primary goals of physiotherapy is to reduce pain caused by a variety of conditions, such as injuries, chronic pain, and post-operative pain. Physiotherapists use a range of techniques, such as manual therapy, modalities, and exercise, to help reduce pain.
- Improve mobility and function: Physiotherapy aims to improve mobility and function by increasing muscle strength, flexibility, and balance. This can help patients with mobility impairments perform daily activities more easily and with less pain.
- Restore Range of Motion: Physiotherapy can help restore the range of motion in joints and muscles that have been affected by injury, surgery, or chronic conditions. This can help patients regain the ability to perform daily activities and hobbies that they may have lost due to their condition.
- Prevent Further Injury: Physiotherapy can help patients prevent further injury by identifying and addressing potential risk factors. Physiotherapists can provide education on proper body mechanics, posture, and injury prevention strategies to help patients stay healthy and active.
- Improve the quality of life: Physiotherapy can have a positive impact on a patient’s quality of life by reducing pain, improving mobility and function, and promoting overall health and well-being. Physiotherapists work closely with patients to develop individualized treatment plans that address their specific needs and goals.
- Promote Healing: Physiotherapy can promote healing by improving circulation, reducing inflammation, and increasing the delivery of nutrients and oxygen to injured tissues. This can help patients recover more quickly from injuries and surgeries and reduce the risk of complications.
Overall, the goals of physiotherapy treatment are to help patients recover from injuries, manage chronic conditions, and improve their overall health and well-being. Physiotherapists work closely with their patients to develop individualized treatment plans that address their specific needs and goals.
Advantages of physiotherapy
- Pain Relief: Physiotherapy is an effective way to manage pain associated with a range of conditions, including musculoskeletal injuries, chronic pain, and postoperative pain.
- Improved Function: Physiotherapy can help individuals improve their ability to perform daily activities, such as walking, standing, and reaching, by improving mobility, strength, and balance.
- Prevent Further Injury: Physiotherapy can help prevent future injuries by addressing underlying risk factors and providing education on proper body mechanics and injury prevention strategies.
- Non-Invasive: Physiotherapy treatments are generally non-invasive and do not involve the use of drugs or surgery, making them a safe and effective treatment option for many individuals.
- Individualized Treatment: Physiotherapy treatment is tailored to the individual’s specific needs, goals, and condition, providing personalized care that addresses their unique concerns.
Disadvantages of physiotherapy
- Time-Consuming: Physiotherapy treatment can be time-consuming, requiring regular appointments and exercises over an extended period.
- Discomfort: Some physiotherapy treatments, such as massage or stretching, can cause temporary discomfort or pain.
- Cost: Physiotherapy treatment can be costly, particularly if an individual requires multiple sessions or treatments.
- Limited Effectiveness: While physiotherapy can be effective for many conditions, it may not provide significant relief or improvement for all individuals.
- Dependent on Patient Effort: The effectiveness of physiotherapy treatment is dependent on the patient’s willingness to participate in exercises and follow through with their treatment plan.
Overall, the advantages of physiotherapy generally outweigh the disadvantages, as physiotherapy is an effective, safe, and non-invasive way to manage pain, improve function, and prevent future injury. While there may be some drawbacks, these are typically outweighed by the benefits of treatment.
Conclusion
Physiotherapy treatment and exercises are designed to help patients recover from injuries, manage chronic pain, and prevent future injuries. Physiotherapists use a variety of techniques, including manual therapy, exercises, and modalities, to address physical conditions and injuries. Physiotherapy exercises are designed to improve mobility, strength, and flexibility. The type of exercise prescribed will depend on the patient’s condition and goals. It is important to consult a physiotherapist to develop an individualized treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs.
FAQs
What is the type of physiotherapy?
Physiotherapy includes different types of treatment approaches that vary depending on the condition, needs, and goals of the patient. Some common types of physiotherapy include:
- Orthopedic physiotherapy: This type of physiotherapy focuses on the treatment of musculoskeletal injuries, such as sprains, strains, fractures, and post-surgical rehabilitation.
- Neurological physiotherapy: This type of physiotherapy aims to help people with neurological disorders, such as stroke, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and spinal cord injuries, improve their movement, balance, and function.
- Cardiovascular and pulmonary physiotherapy: This type of physiotherapy focuses on the rehabilitation of people with heart and lung conditions, such as heart attacks, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and asthma, to improve their cardiovascular and respiratory function.
- Pediatric physiotherapy: This type of physiotherapy specializes in the treatment of children with physical disabilities, developmental delays, and injuries to help them achieve their optimal physical potential.
- Geriatric physiotherapy: This type of physiotherapy is focused on the treatment of elderly people with mobility and balance issues, chronic pain, and age-related conditions such as arthritis and osteoporosis.
- Sports physiotherapy: This type of physiotherapy deals with sports-related injuries, such as ligament sprains, muscle strains, and overuse injuries, to help athletes recover from injuries and improve their athletic performance.
These are some of the common types of physiotherapy, but there are many other specialized areas, such as women’s health, oncology, and occupational therapy. A physiotherapist can help determine which type of physiotherapy is best for a patient’s needs.
What is the role of exercise therapy in physiotherapy?
Exercise therapy is an essential component of physiotherapy and plays a crucial role in the rehabilitation and management of various musculoskeletal, neurological, cardiovascular, and respiratory conditions. Exercise therapy involves the use of specific exercises, movements, and activities to help patients regain strength, flexibility, endurance, balance, and coordination and improve their overall physical function and quality of life.
The role of exercise therapy in physiotherapy includes the following:
- Restoring and improving mobility: Exercise therapy helps to restore normal joint range of motion, increase muscle strength, and improve flexibility and balance, which can enhance overall mobility.
- Reducing pain and inflammation: Exercise therapy can help reduce pain and inflammation by strengthening and stretching muscles and joints, improving circulation, and releasing endorphins.
- Preventing or managing chronic diseases: Exercise therapy can help manage chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and arthritis by improving blood sugar control, reducing blood pressure and cholesterol levels, and reducing joint stiffness.
- Improving cardiovascular and respiratory function: Exercise therapy can improve cardiovascular and respiratory function by increasing endurance, improving lung capacity, and reducing shortness of breath.
- Enhancing mental health: Exercise therapy can enhance mental health by reducing stress, anxiety, and depression and improving mood, self-esteem, and overall quality of life.
- Promoting healthy aging: Exercise therapy can promote healthy aging by helping older adults maintain mobility, prevent falls, and improve cognitive function.
Overall, exercise therapy is an effective and evidence-based intervention that can help patients achieve their physical and functional goals and improve their overall health and well-being.
Does physical therapy really work?
Yes, physical therapy can be very effective for many conditions and injuries. Physical therapy is a non-invasive, non-pharmaceutical approach to treating pain, injury, and disability. It is often used as a first-line treatment for many musculoskeletal, neurological, cardiovascular, and respiratory conditions.
Research has shown that physical therapy can be effective for many conditions, including:
- Low back pain
- Neck pain
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Rotator cuff injuries
- Tennis elbow
- Hip and knee replacement surgeries
- Stroke
- Parkinson’s disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Physical therapy is based on evidence-based practices and customized to each patient’s individual needs and goals. Physical therapists use a variety of techniques and exercises to improve mobility, strength, flexibility, balance, and coordination. They also work to manage pain, swelling, and inflammation.
Physical therapy can also help prevent future injuries or disabilities by educating patients on proper posture, body mechanics, and exercise techniques. It is often used as part of a multidisciplinary approach to healthcare, working alongside other healthcare professionals such as doctors, chiropractors, and occupational therapists.
Is physical therapy painful?
Physical therapy is not supposed to hurt, but you might feel some discomfort or mild soreness during or after a session. Physical therapy is designed to help you feel better, not make you feel worse. If you feel uncomfortable during an exercise, let your therapist know so they can adjust it for you. Your therapist can also give you ways to manage any pain or swelling, like using ice or heat. If you feel really bad, tell your therapist right away so they can make sure you’re okay. Overall, physical therapy should be comfortable and help you feel better, not hurt you.
What kind of people need physical therapy?
Physical therapy can help a lot of different people with different problems. Here are some examples:
- Athletes: People who play sports and get hurt might need physical therapy to help them get better.
- People who had surgery: People who get surgery might need physical therapy to help them feel better and move better.
- People with chronic pain: People who have had pain for a long time might need physical therapy to help them manage their pain and move better.
- People with neurological conditions: People with conditions that affect their brain and nerves might need physical therapy to help them feel better and move better.
- People with breathing problems: People who have trouble breathing might need physical therapy to help them breathe better and feel better.
- People who have trouble with balance or walking: People who have trouble balancing or walking might need physical therapy to help them feel better and move better.